PROJECT TYPE: Secondary
DURATION : 3 months
Haloacetic acids (HAAs) have recently been included as one of the quality parameters to be determined in drinking water (RD 3/2023), which is why the Water Consortium is interested in knowing the concentrations of this parameter obtained in the different DWTPs, as well as knowing the processes by which haloacetic acids are generated, variables on which their formation depends, formation reactions, relationships with other disinfection products generated (THMs, bromates…), values found in different types of processes (with different pre-oxidants and disinfectants, if they are adsorbed on activated carbon, if they can be eliminated by exchange resins, etc.).) values found in different types of processes (with different pre-oxidants and disinfectants, if they are adsorbed on activated carbon, if they can be eliminated by means of exchange resins, etc.).
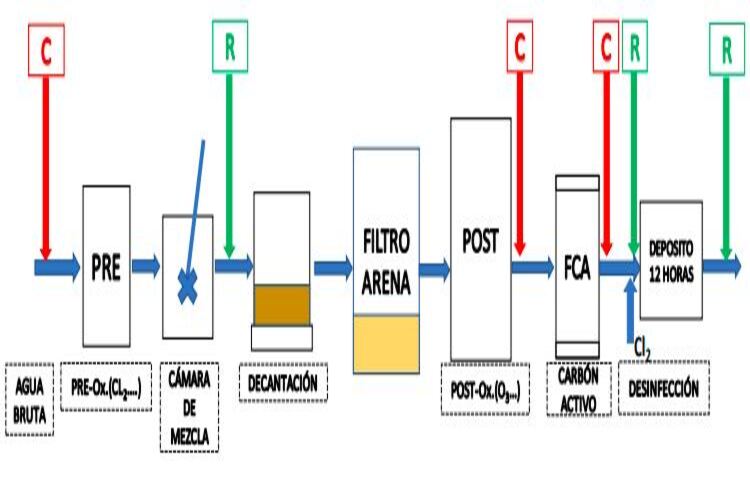
In each of the configurations to be developed in the CATABB, the study of the THM and HAA formation potential will be carried out. For this purpose, several representative samples will be taken at the sampling points selected for this purpose: crude, post-oxidation outlet and activated carbon outlet. The samples taken will be overchlorinated on the spot and preserved at a constant temperature (10 ºC and 25º). Finally, after the time established for each of the samples from the different points has elapsed, the reaction will be cut off and preserved until the day of its respective analysis. The study of the formation potential of DBPs will be the basis for establishing the formation mechanisms in the key processes of the DWTPs.
The expected results would be to characterize the formation capacity at key points in the process of a DWTP, considering the different variants in terms of water resource, concentration and type of oxidant, and to assess the effect of plant operating conditions on DBPs formation. The aim is to assess the effect of the plant’s operating conditions on the formation of DBPs. From these results it will be possible to define the operating conditions that minimize the formation of DBPs. In addition, this study will emphasize the analysis of the influence of temperature and the significance of the key operations on the formation of these compounds.